4.2 KiB
Introduction
In this first lab we are going to do the basics. We'll:
- Log into AWS
- Use cloudshell (as this has all your credentials set up already)
- Get your environment ready to run terraform/tofu
- Run a simple example
Log into AWS
First of all head to https://aws.amazon.com and sign into your console. The next thing to do is check that you are working inthe correct region. For this lab everything is coded for eu-west-1 (Ireland) so make sure you select the correct region at the top right hand of the page.
Once in this region we are setup for the following labs.
Note
We'll be creating infrastructure throughout and AWS does charge for your actual usage
Open CloudShell
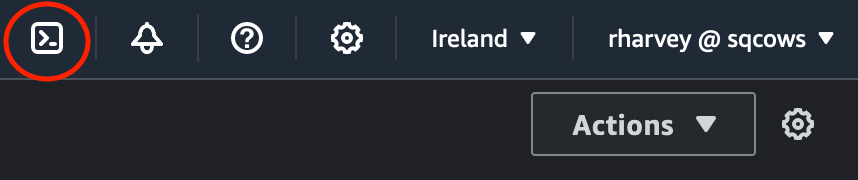
For these labs we are going to use the AWS supplied CloudShell, now you can do this from your own machine, however, you'll need to setup the AWS CLI tool and AWS credentials which is beyond the scope of these labs. The nice thing about CloudShell is that it's already configured with your credentials for accessing AWS resources. You also launch this by heading up to the main bar in the AWS console and clicking the icon highlighted below:
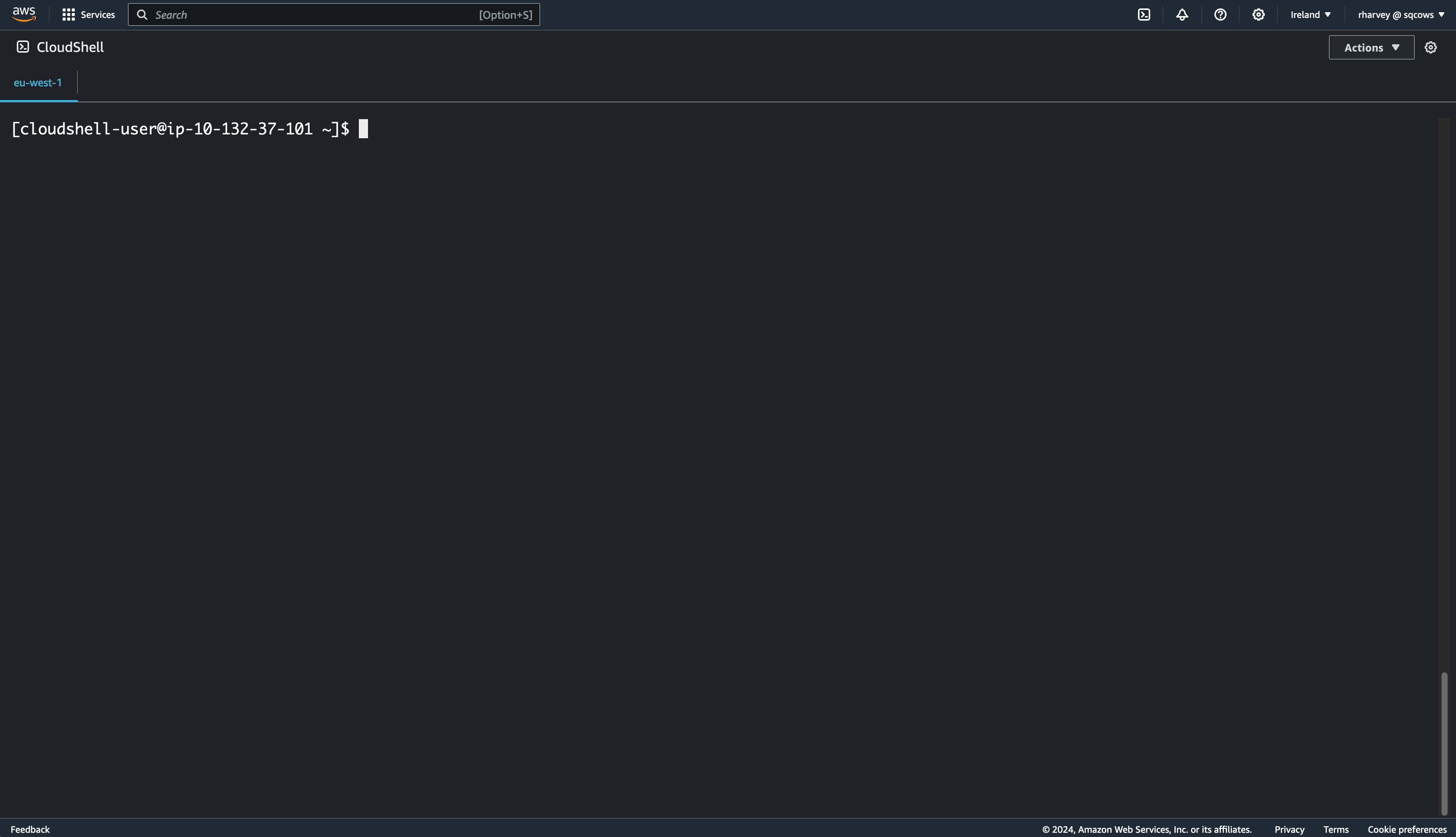
Once launched you can hit the arrow to break the shell out into it's own browser tab. I personally find it easier to work this way. It's also good to know there is no charge to run CloudShell. It'll look a little like this when opened:
Right lets get you setup to run terraform or openTofu! You only need to do one of these so choose your tool of choice. I lean toward using tofu as it's fully open source, but if you want some of the newer features in terraform 1.8.0 and higher the guide is here for you also.
Note
Periodically you CloudShell is rebuilt and anything thats not stored in your home directory will be deleted, for this reason the method's below store the tooling in your home directory.
Install Terraform
First we are going to install a tool that make's it easy to install the binaries for Terraform. Copy and Paste the below into your CloudShell:
git clone https://github.com/tfutils/tfenv.git ~/.tfenv
mkdir ~/bin
ln -s ~/.tfenv/bin/* ~/bin/
Find the latest version and install it (at the time of writing it was 1.8.0):
tfenv list-remote
tfenv install 1.8.0
tfenv use 1.8.0
Now test it's all working:
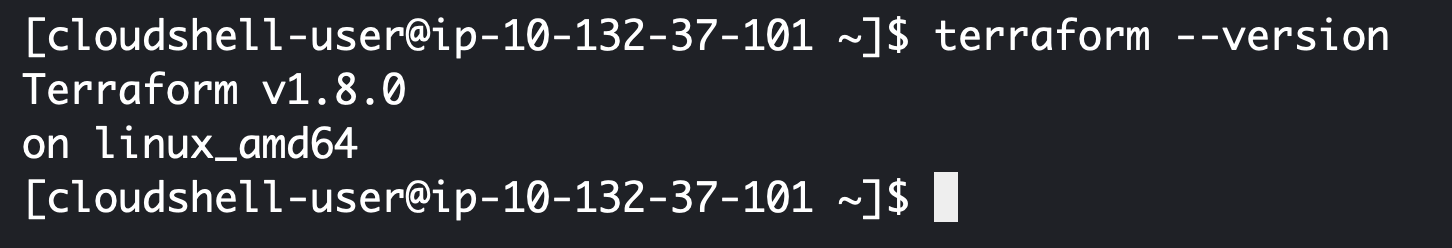
terraform --version
The output should look likt e following screenshot:
Install Tofu
If like me you prefer to use open source tools this is how to make tofu persist in CloudShell, Copy and Paste the following into your terminal:
# Download the installer script:
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -fsSL https://get.opentofu.org/install-opentofu.sh -o install-opentofu.sh
# Alternatively: wget --secure-protocol=TLSv1_2 --https-only https://get.opentofu.org/install-opentofu.sh -O install-opentofu.sh
# Give it execution permissions:
chmod +x install-opentofu.sh
# Please inspect the downloaded script
# Run the installer:
./install-opentofu.sh --install-method rpm
# Remove the installer:
rm install-opentofu.sh
# Make Tofu remain in your path after reboots
mkdir ~/bin
sudo mv /usr/bin/tofu ~/bin
Now test it's all working:
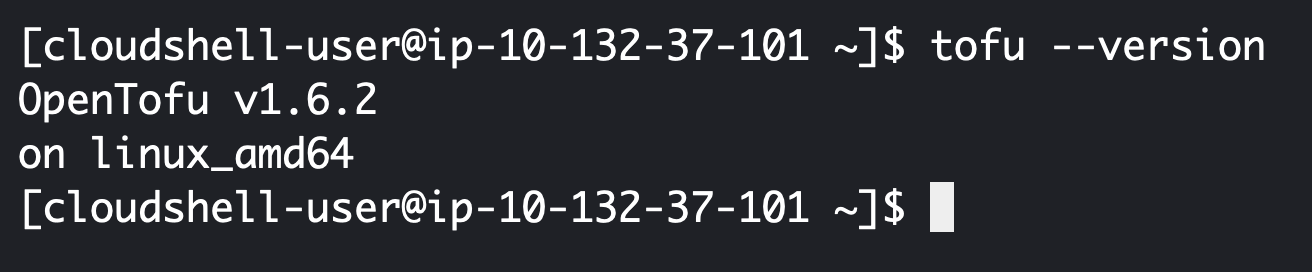
tofu --version
The output should look likt e following screenshot:
Now your tooling is installed and should survice you reconnecting to CloudShell.
Test Deployment
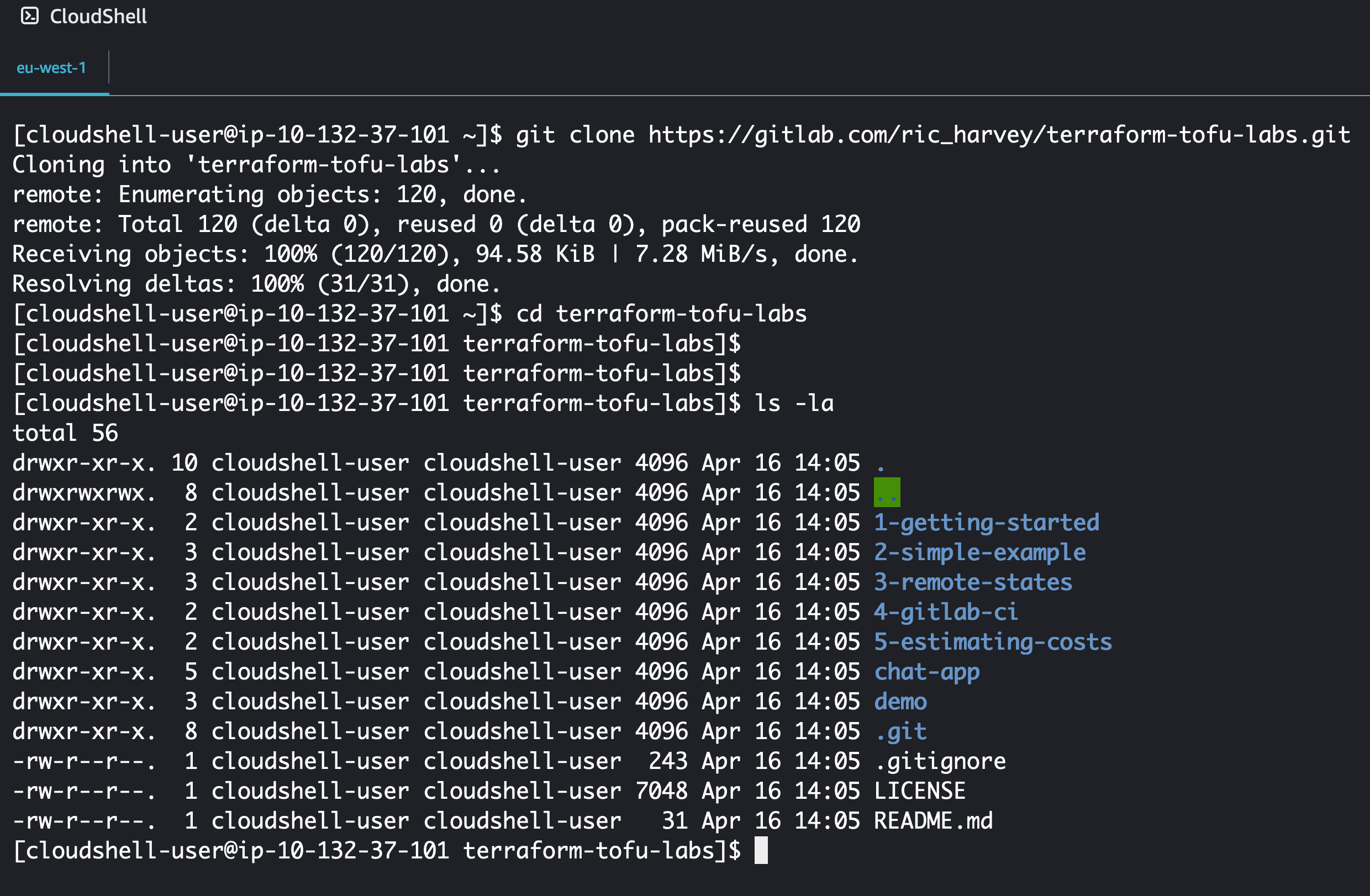
Before we deploy to AWS we need to pull the code down from GitLab onto your CloudShell. To do this run the follwoing commands:
git clone https://gitlab.com/ric_harvey/terraform-tofu-labs.git
cd terraform-tofu-labs
The output will look like the following:
Now lets run some code.
Note
You can replace the commands for
terraformfromtofuif you are running that version
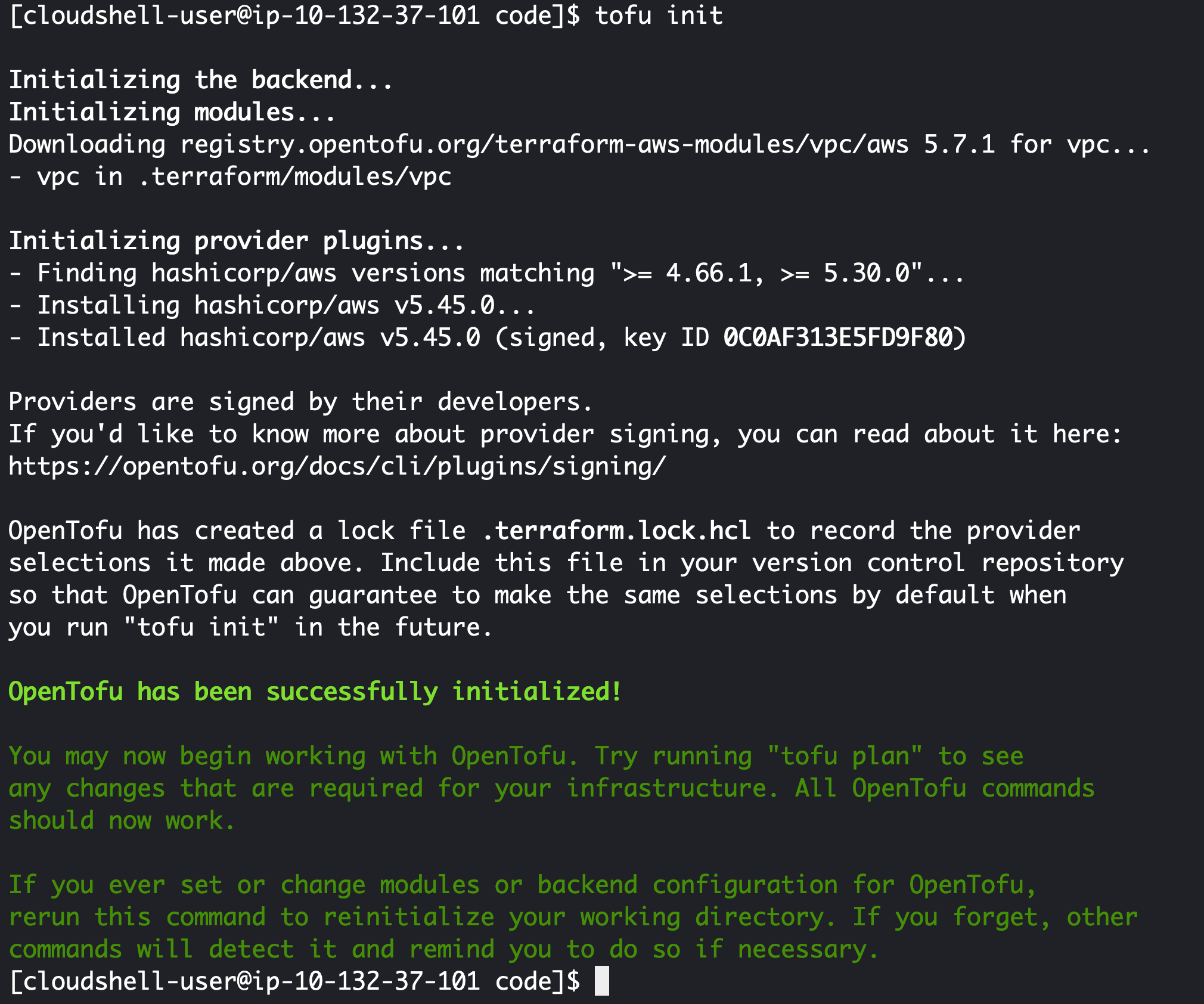
First lets initialise our terraform/tofu environment:
cd 1-getting-started/code/
tofu init